Thin Layer Chromatography: Principle, Parts, Steps, Uses

Chromatography is an important biophysical technique that enables the separation, identification, and purification of the components of a mixture for qualitative and quantitative analysis.
In this physical method of separation, the components to be separated are distributed between two phases, one of which is stationary (stationary phase) while the other (the mobile phase) moves in a definite direction. Depending upon the stationary phase and mobile phase chosen, they can be of different types.
Table of Contents
Interesting Science Videos
What is Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)?
Thin Layer Chromatography can be defined as a method of separation or identification of a mixture of components into individual components by using finely divided adsorbent solid / (liquid) spread over a plate and liquid as a mobile phase.
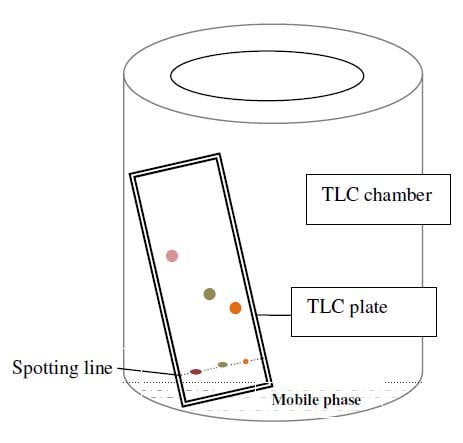
Principle of Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
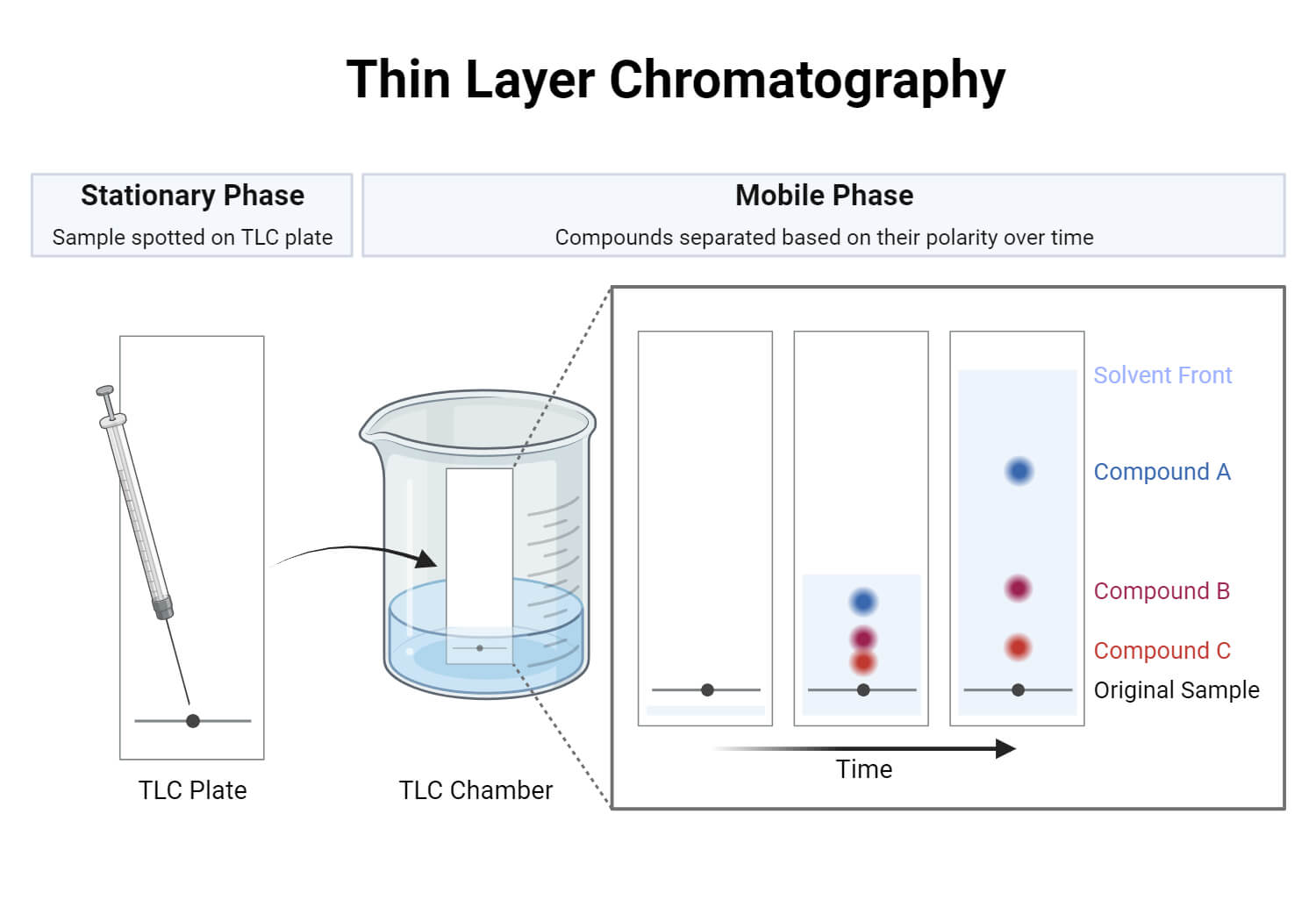
- Thin-layer chromatography is performed on a sheet of glass, plastic, or aluminium foil, which is coated with a thin layer of adsorbent material, usually silica gel, aluminium oxide (alumina), or cellulose. This layer of adsorbent is known as the stationary phase.
- After the sample has been applied on the plate, a solvent or solvent mixture (known as the mobile phase) is drawn up the plate via capillary action. Because different analytes ascend the TLC plate at different rates, separation is achieved.
- It is thus based on the principle of adsorption chromatography or partition chromatography or combination of both, depending on adsorbent, its treatment and nature of solvents employed. The components with more affinity towards stationary phase travels slower. Components with less affinity towards stationary phase travels faster.
- Once separation occurs, the individual components are visualized as spots at a respective level of travel on the plate. Their nature or character is identified by means of suitable detection techniques.
Components of Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
TLC system components consists of:
- TLC plates, preferably ready made with a stationary phase: These are stable and chemically inert plates, where a thin layer of stationary phase is applied on its whole surface layer. The stationary phase on the plates is of uniform thickness and is in a fine particle size.
- TLC chamber- This is used for the development of TLC plate. The chamber maintains a uniform environment inside for proper development of spots. It also prevents the evaporation of solvents, and keeps the process dust free.
- Mobile phase- This comprises of a solvent or solvent mixture The mobile phase used should be particulate-free and of the highest purity for proper development of TLC spots. The solvents recommended are chemically inert with the sample, a stationary phase.
- A filter paper- This is moistened in the mobile phase, to be placed inside the chamber. This helps develop a uniform rise in a mobile phase over the length of the stationary phase.
Procedure of Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
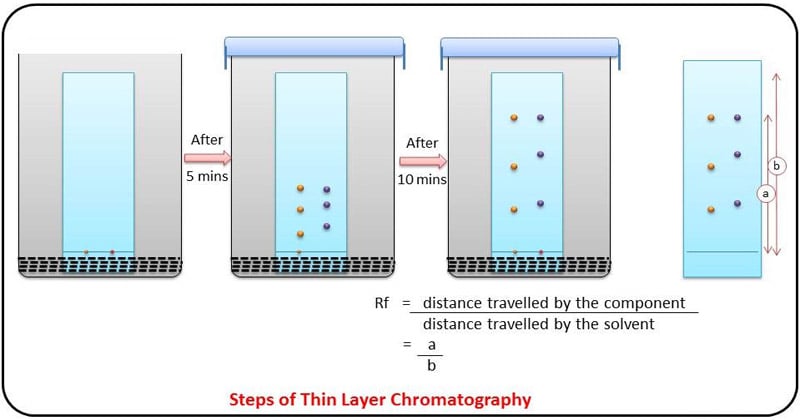
The stationary phase is applied onto the plate uniformly and then allowed to dry and stabilize. These days, however, ready-made plates are more commonly used.
- With a pencil, a thin mark is made at the bottom of the plate to apply the sample spots.
- Then, samples solutions are applied on the spots marked on the line in equal distances.
- The mobile phase is poured into the TLC chamber to a leveled few centimeters above the chamber bottom.
- A moistened filter paper in mobile phase is placed on the inner wall of the chamber to maintain equal humidity (and also thereby avoids edge effect).
- Now, the plate prepared with sample spotting is placed in TLC chamber so that the side of the plate with the sample line is facing the mobile phase. Then the chamber is closed with a lid.
- The plate is then immersed, such that the sample spots are well above the level of mobile phase (but not immersed in the solvent) for development.
- Sufficient time is given for the development of spots.
- The plates are then removed and allowed to dry.
- The sample spots are then seen in a suitable UV light chamber, or any other methods as recommended for the given sample.
Some common techniques for visualizing the results of a TLC plate include
- UV light
- Iodine Staining: is very useful in detecting carbohydrates since it turns black on contact with Iodine
- KMnO4 stain (organic molecules)
- Ninhydrin Reagent: often used to detect amino acids and proteins
Retention Factor (Rf ) Value
- The behaviour of a compound on a TLC is usually described in terms of its relative mobility or Rf value.
- Rf or Retention factor is a unique value for each compound under the same conditions.
- The Rf for a compound is a constant from one experiment to the next only if the chromatography conditions below are also constant:
- solvent system
- adsorbent
- thickness of the adsorbent
- amount of material spotted
- temperature
- Since these factors are difficult to keep constant from experiment to experiment, relative Rf values are generally considered.
- Relative Rf” means that the values are reported relative to a standard.
- The Rf value is calculated using the following equation:
Applications of Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
- In monitoring the progress of reactions
- Identify compounds present in a given mixture
- Determine the purity of a substance.
- Analyzing ceramides and fatty acids
- Detection of pesticides or insecticides in food and water
- Analyzing the dye composition of fibers in forensics
- Assaying the radiochemical purity of radiopharmaceuticals
- Identification of medicinal plants and their constituents
Advantages of Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
- It is a simple process with a short development time.
- It helps with the visualization of separated compound spots easily.
- It helps in isolating of most of the compounds.
- The separation process is faster and the selectivity for compounds is higher (even small differences in chemistry is enough for clear separation).
- The purity standards of the given sample can be assessed easily.
- It is a cheaper chromatographic technique.
Limitations of Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
- It cannot tell the difference between enantiomers and some isomers.
- In order to identify specific compounds, the Rf values for the compounds of interest must be known beforehand.
- TLC plates do not have long stationary phases. Therefore, the length of separation is limited compared to other chromatographic techniques.
References
- https://owlcation.com/stem/tlc-thin-layer-chromatography-Principle-Procedure
- https://www.utsc.utoronto.ca/webapps/chemistryonline/production/tlc.php
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thin-layer_chromatography
- https://chem.libretexts.org/Demos%2C_Techniques%2C_and_Experiments/General_Lab_Techniques/Thin_Layer_Chromatography
- https://www.slideshare.net/LavakusaBanavatu/thin-layer-chromatography-43293607
About Author





